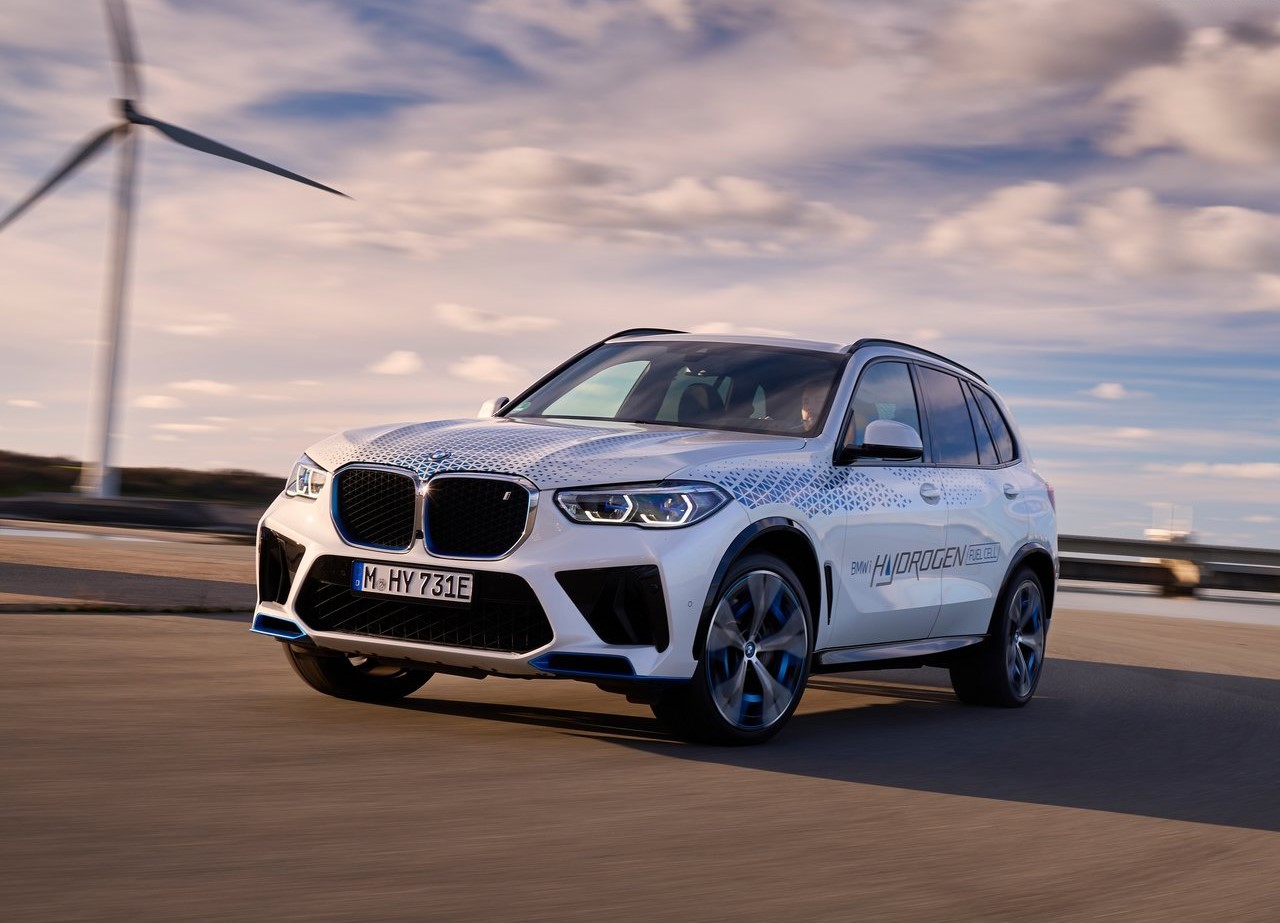
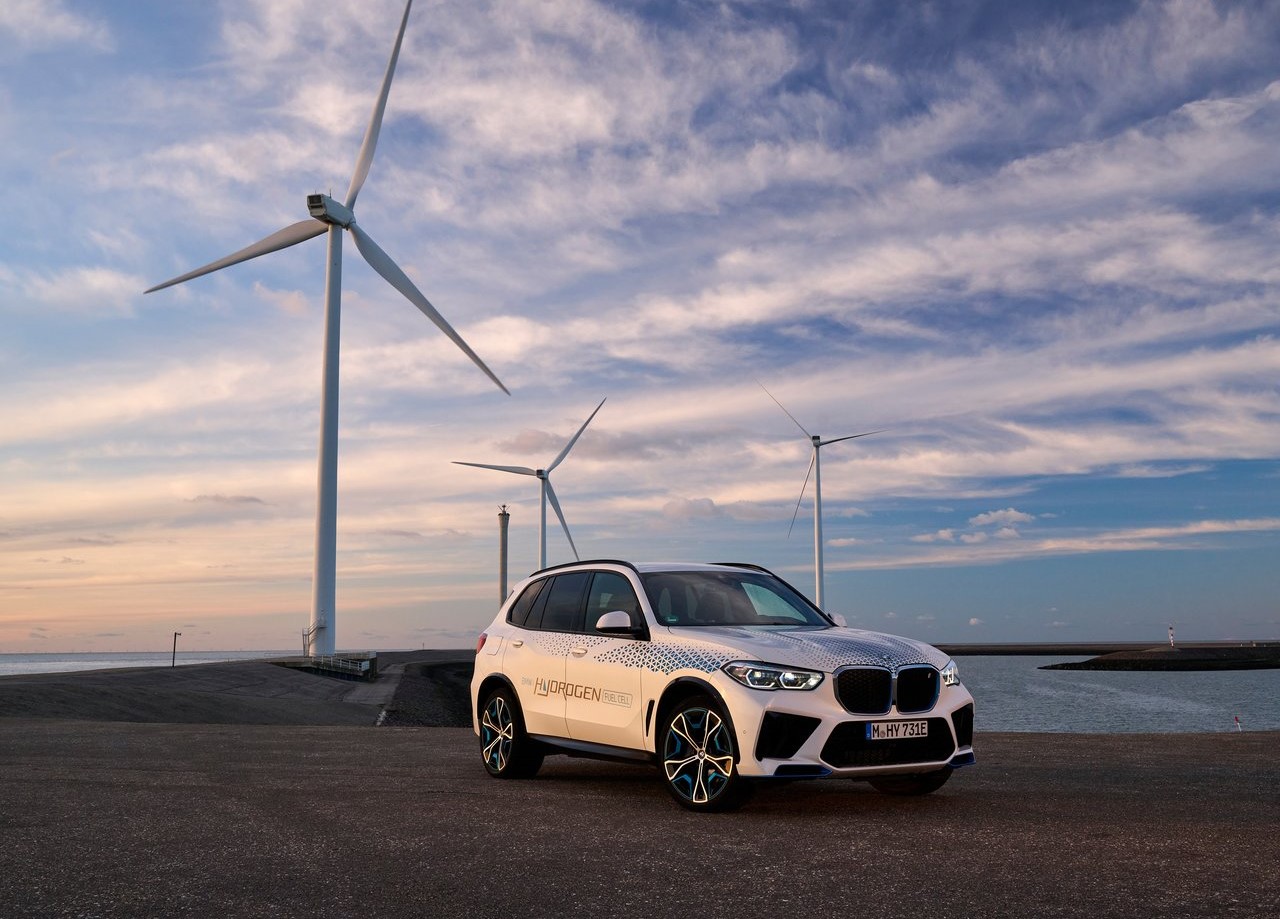
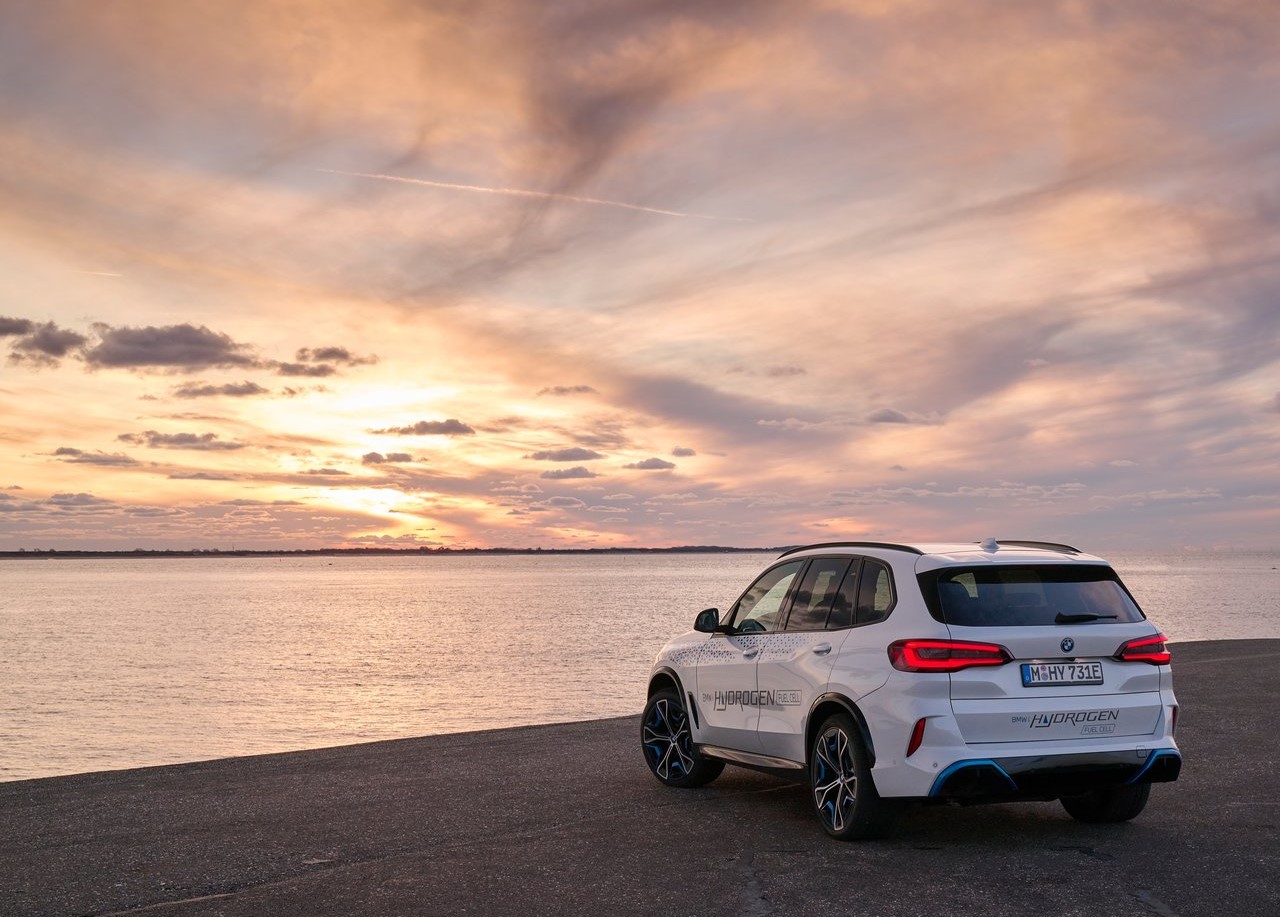
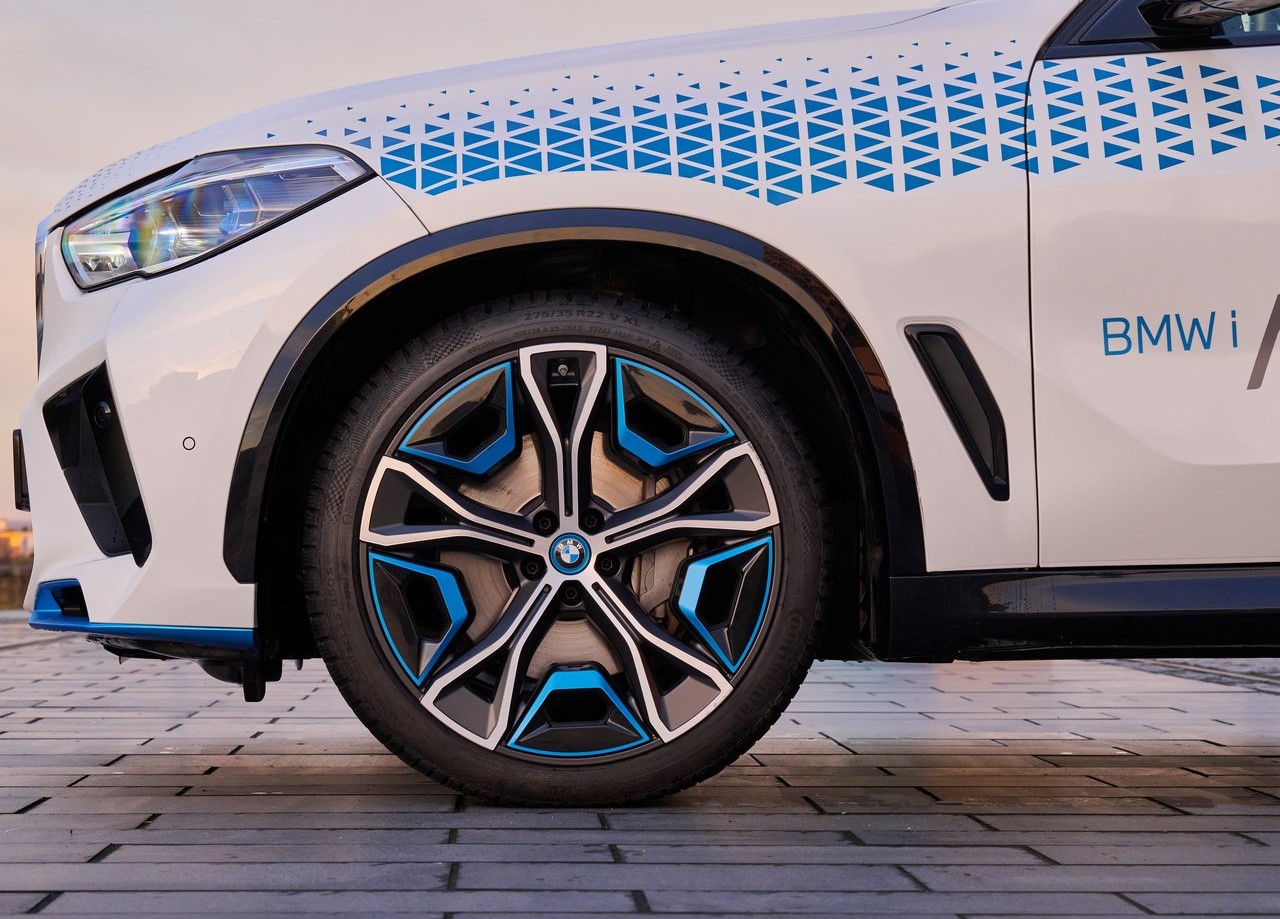
During the IAA exhibition in 2019, a concept version of the BMW iX5 Hydrogen, which was built on the foundation of the existing BMW X5, was first presented. Early prototypes were subsequently made available for guests to test drive as shuttle cars during the IAA Mobility 2021.
The BMW Group's superior technological competence in the field of electric motor systems is further demonstrated by its hydrogen fuel cell technology. The development of hydrogen fuel cell technology is being actively pursued by the BMW Group as a potential supplement to locally emission-free private transportation.
BMW's technological expertise
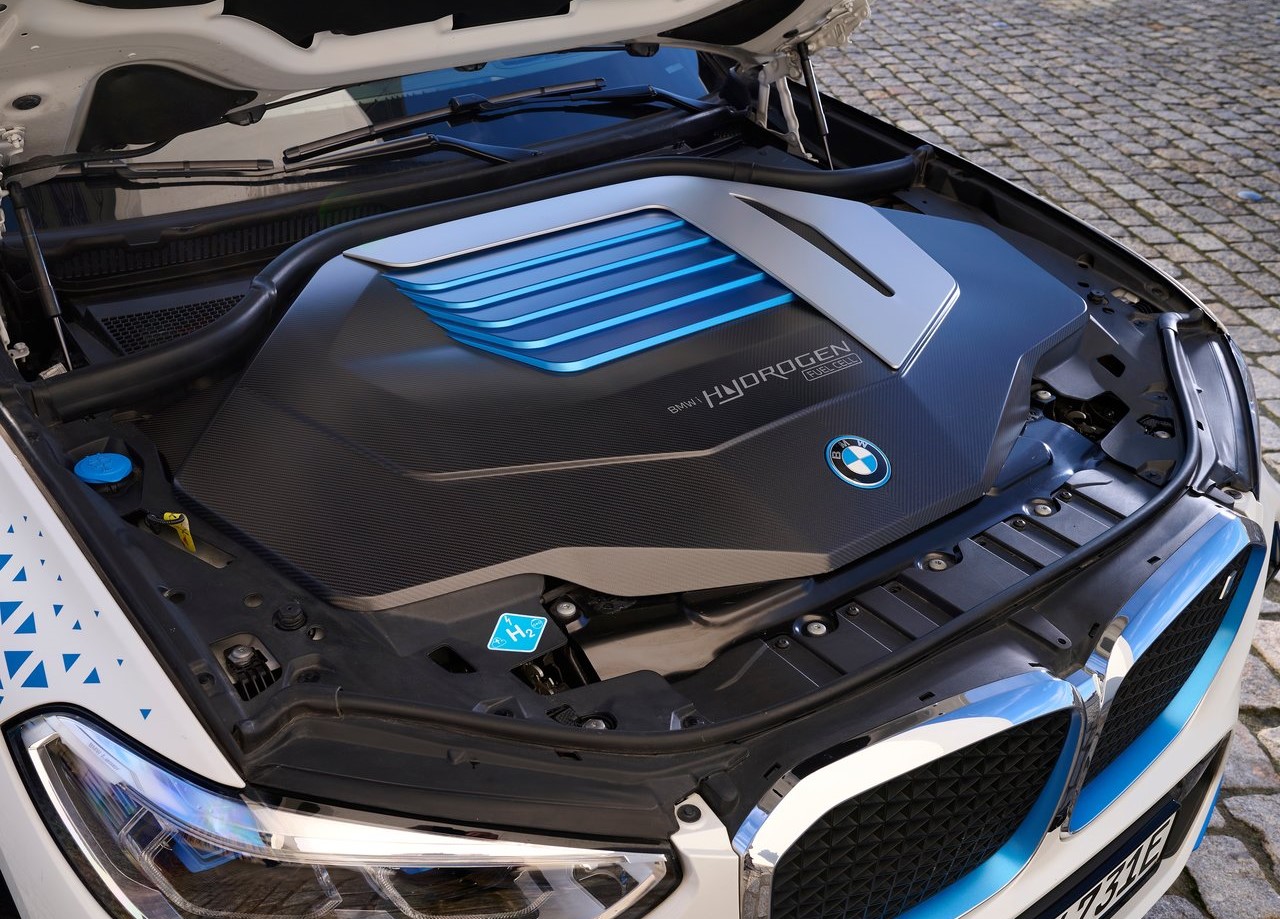
The BMW Group's own hydrogen competence center in Munich manufactures the incredibly effective fuel cell systems for the test fleet. One of the key components of the BMW iX5 Hydrogen, this technology produces a high continuous output of 125 kW/170 horsepower.
Gaseous oxygen from the air and hydrogen from the tanks interact chemically inside the fuel cell. The effectiveness of the driving mechanism depends critically on maintaining a consistent supply of both substances to the fuel cell membrane. The BMW Group has created unique hydrogen components for its new fuel cell system in addition to the technological counterparts of features present in combustion engines, such as charge air coolers, air filters, control units, and sensors. The high-speed compressor with a turbine and the high-voltage coolant pump are two examples of these.
The Toyota Motor Company is the supplier of the individual fuel cells to the BMW Group. Since 2013, the two businesses have been working together on fuel cell propulsion systems. Their long-standing cooperation has been characterized by trust.
Depending on the specific fuel cells, there are two primary processes in the production of fuel cell systems. The cells are initially put together into a stack of fuel cells. The final stage is to assemble every component into a full fuel cell system.
The procedure of stacking the fuel cells is virtually totally automated. The stack is squeezed mechanically with a force of five tonnes and placed in a housing after each component has been checked for damage. Sand casting is used to create the stack housing at the light metal foundry at BMW Group Plant Landshut.
For this, a procedure especially created for this small-series car involves pouring molten aluminum into a mould constructed from compressed sand combined with resin.
The Landshut plant's cast plastic components and light-alloy castings are used to create the pressure plate, which feeds hydrogen and oxygen to the fuel cell stack. Around the stack housing, the pressure plate creates an airtight and watertight seal.
A voltage test and in-depth testing of the chemical reaction occurring inside the cells are both performed as part of the fuel cell stacks' final construction. At the assembly section, all the various parts are finally assembled to create the full system.
Other parts are installed at this system assembly step, including the compressor, the fuel-cell system's anode and cathode, the high-voltage coolant pump, and the wiring harness.
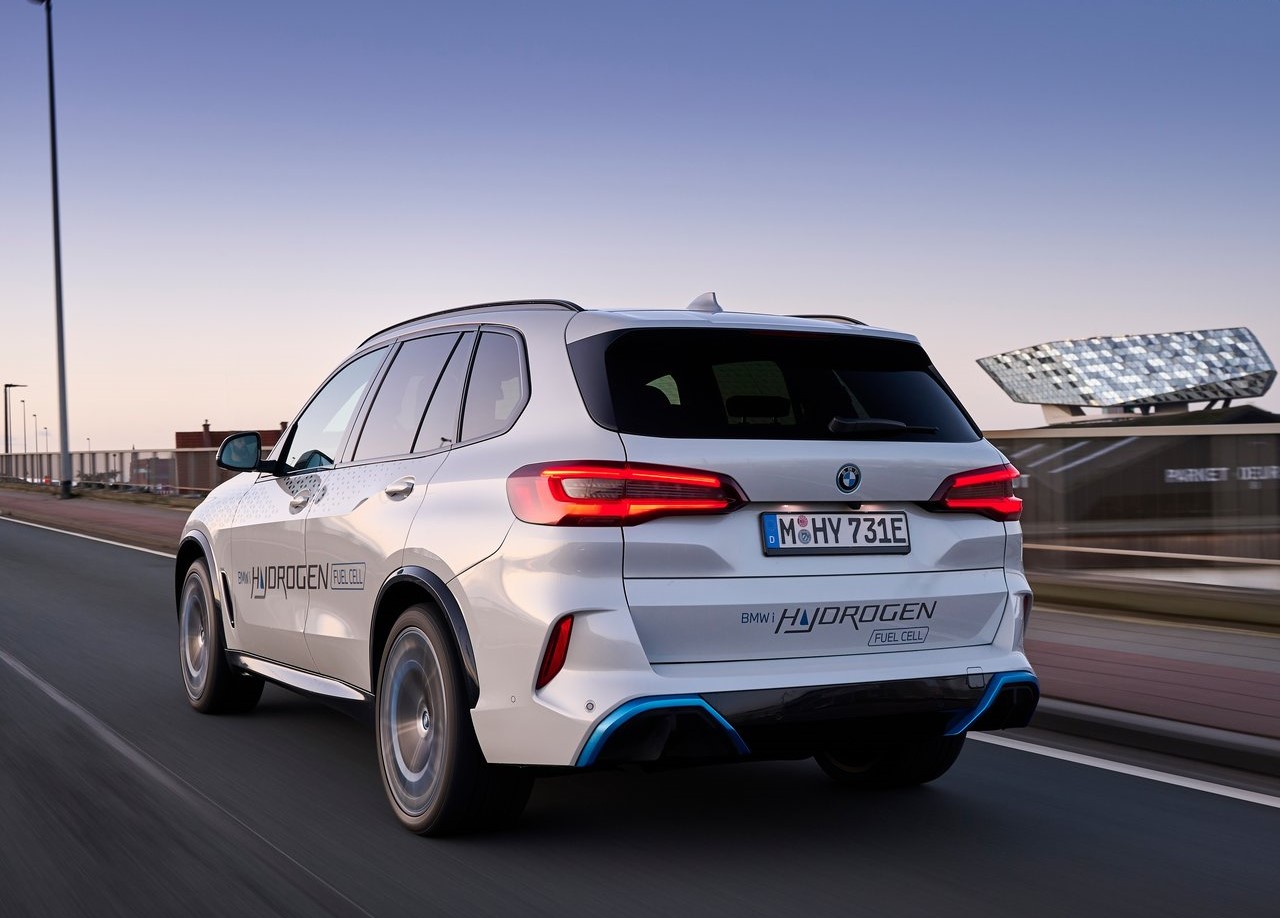
The powertrain transmits a maximum output of 295kW / 401 hp onto the road thanks to a highly integrated drive unit using fifth-generation BMW eDrive technology (the electric motor, transmission, and power electronics are grouped together in a compact housing) at the rear axle and a power battery with lithium-ion technology developed specifically for this vehicle. The motor also functions as a generator during the coasting overrun and braking phases, recharging a power battery.
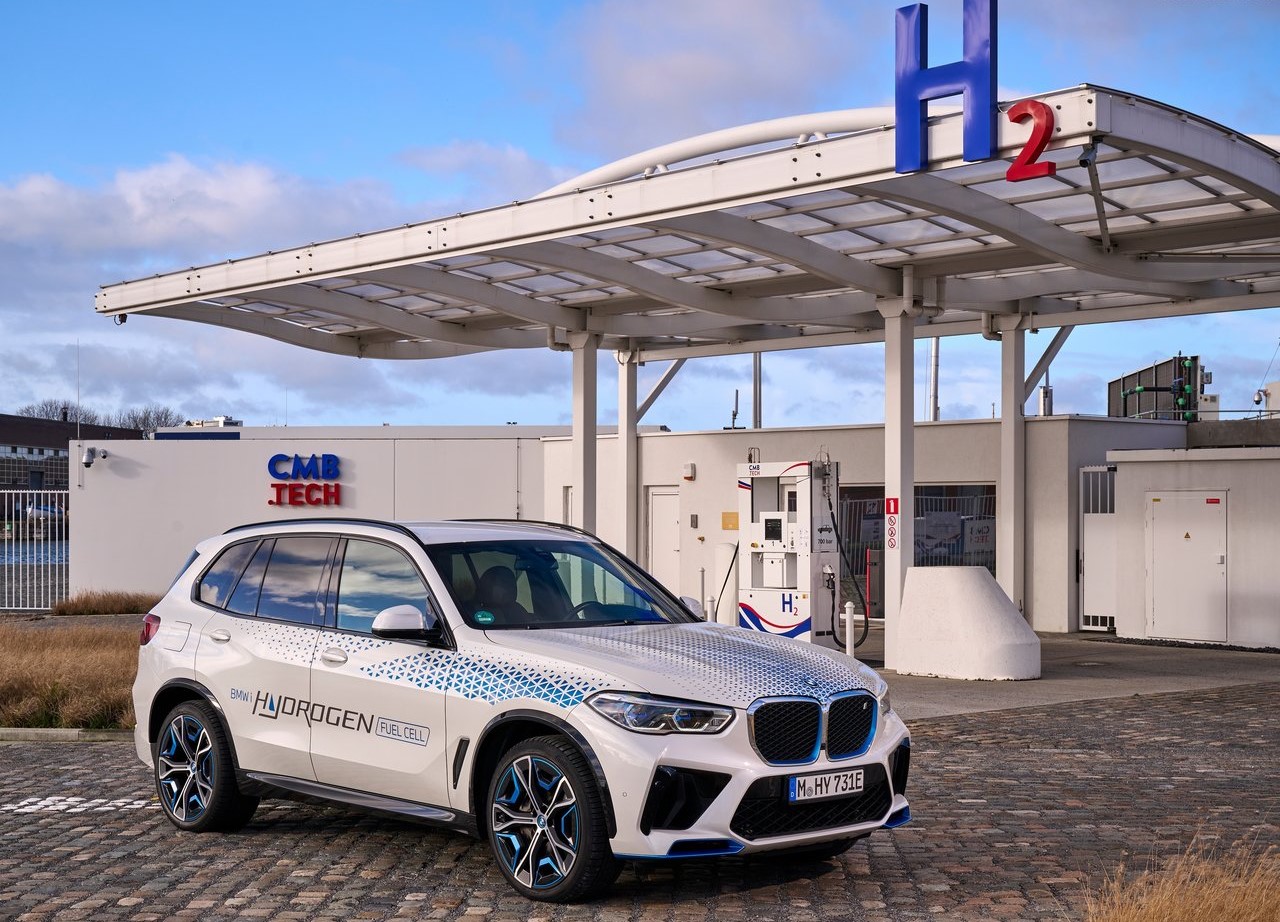
Hydrogen allows rapid re-fuelling
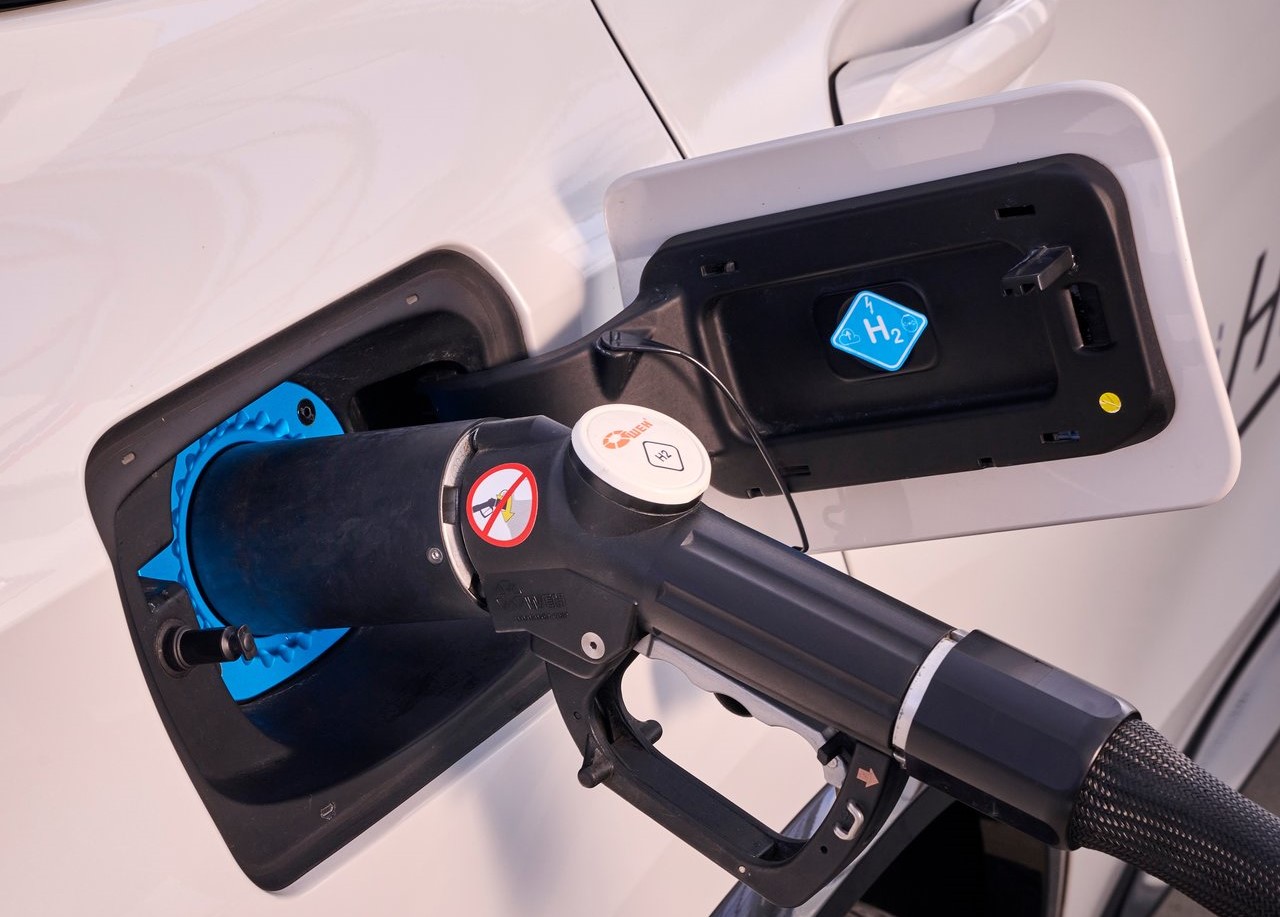
Two 700-bar tanks constructed of carbon-fiber reinforced plastic are used to hold the hydrogen needed to power the fuel cell (CFRP). Combined, they can contain about six kilos of hydrogen, which will give the BMW iX5 Hydrogen a WLTP cycle range of 504 kilometers (313 miles). The hydrogen tanks can be filled in only three to four minutes, allowing the BMW iX5 Hydrogen to deliver the same thrilling driving experience for which BMW is known across long distances with only a few brief stops along the way.
Summary of the technical data, performance, fuel consumption and range figures for the BMW iX5 Hydrogen
-
Maximum output of overall drive system: 295 kW/401 hp
-
Electric continuous output of the fuel-cell system: 125 kW/170 hp
-
Maximum output of the battery (lithium-ion technology): 170 kW/231 hp
-
Maximum output of the highly integrated electric drive unit: 295 kW/401 hp
-
Capacity of the hydrogen tanks: 6 kg hydrogen (gaseous)
-
Acceleration 0-100 km/h (62 mph) < 6 s
-
Top speed: Over 180 km/h (112 mph)
-
Hydrogen consumption in the WLTP cycle: 1.19 kg/100 km
-
Range in the WLTP cycle: 504 km (313 miles)











.webp)

.jpg)